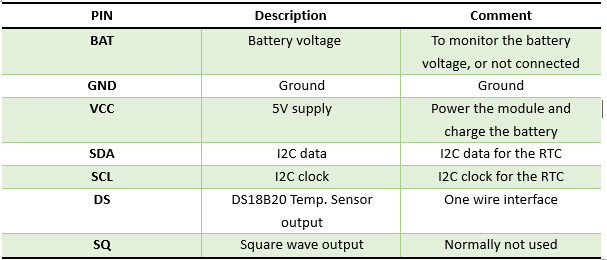
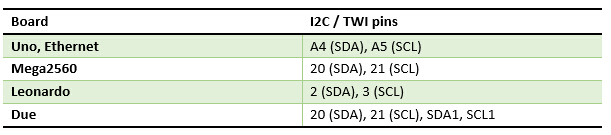
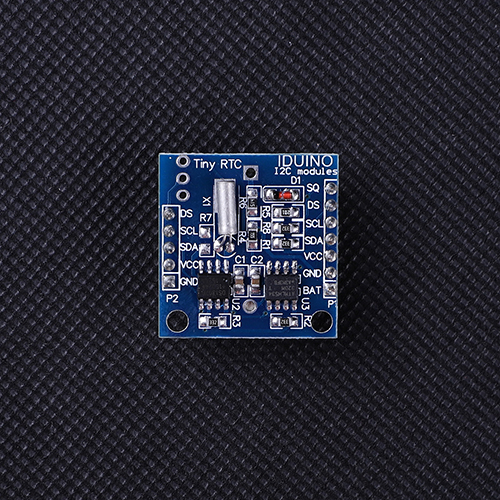
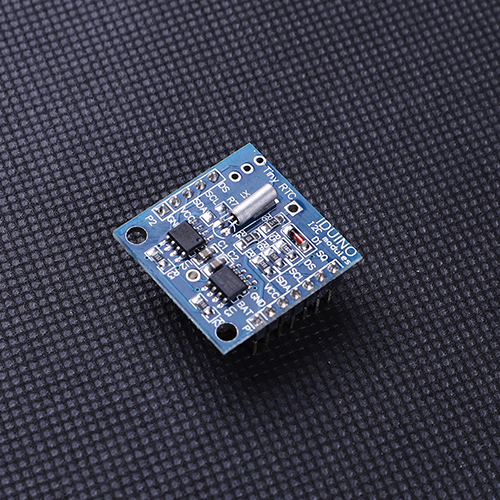
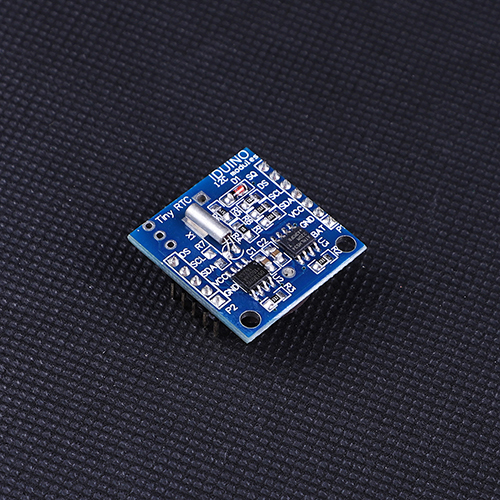
There are three
examples code for the RTC , the EEPROM, and the DS18B20 temperature sensor.
Only the
DS18B20 temperature sensor’s example, the DS pinout is used.
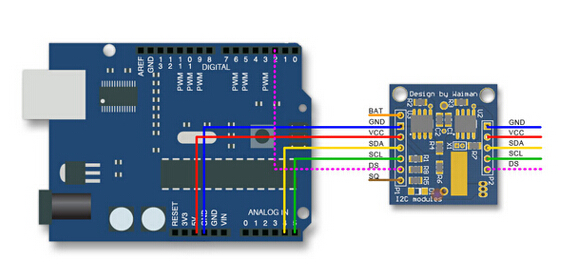
Wire connection as below:
First example for the RTC:
#include
#include
void printDateTime(DateTime dateTime);
RTC_DS1307 RTC;
void setup (void){
Serial.begin(9600);
Wire.begin();
RTC.begin();
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
int instruct = Serial.read();
switch (instruct) {
case 'D': {
DateTime now = RTC.now();
printDateTime(now);
break;
} case 'S':
RTC.set(RTC_MONTH, 6);
RTC.set(RTC_HOUR, 16);
break;
}
}
}
void printDateTime(DateTime dateTime) {
Serial.print(dateTime.year(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(dateTime.month(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(dateTime.day(), DEC);
Serial.print(' ');
Serial.print(dateTime.hour(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(dateTime.minute(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(dateTime.second(), DEC);
Serial.println();
}
Second example for the EEPROM:
#include
#include
#include
AT24Cxx AT24C32(0x50);
RTC_DS1307 RTC;
void setup (void){
Serial.begin(9600);
Wire.begin();
RTC.begin();
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
int instruct = Serial.read();
switch (instruct) {
case 'P':
{
AT24C32.WriteMem(0, 0x04);
break;
}
case 'G':
{
char buffer[3];
AT24C32.ReadMem(0, buffer, 3);
Serial.print(2000 + buffer[2], DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(buffer[1], DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(buffer[0], DEC);
Serial.println();
break;
}
case 'F':
{
DateTime now = RTC.now();
char buffer[3];
buffer[0] = now.day();
buffer[1] = now.month();
buffer[2] = now.year() - 2000;
AT24C32.WriteMem(0, buffer, 3);
break;
}
}
}
}
Third example for the LM75:
#include
#include
LM75 sensor(LM75_ADDRESS | 0b000);
const int OSPIN = 6;
void setup (void){
pinMode(OSPIN, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
Wire.begin();
sensor.tos(47.5);
sensor.thyst(42);
}
void loop() {
if (Serial.available() > 0) {
int instruct = Serial.read();
int OSValue = HIGH;
OSValue = digitalRead(OSPIN);
if (OSValue == LOW)
Serial.println("Over heating!");
switch (instruct) {
case 'T':
Serial.print("Current temp: ");
Serial.print(sensor.temp());
Serial.println(" C");
break;
}
}
}